Filtering: Searching the List of Links
In this section, we’ll implement a search feature and learn about the filtering capabilities of our GraphQL API.
Preparing the React components
The search will be available under a new route and implemented in a new React component.
Again, this is a pretty standard setup. You’re rendering an
input field where the user can type a search string.
The Search component uses the useState hook to hold a
search term supplied by the user. The setSearchFilter
functions is called in the onChange event on the input to
update this value.
The component is also looking for a variable called data
which it iterates over to render Link components with the
search results. We’ll define and execute the query a bit
later.
We can now navigate to the search feature using the search
button in the Header:
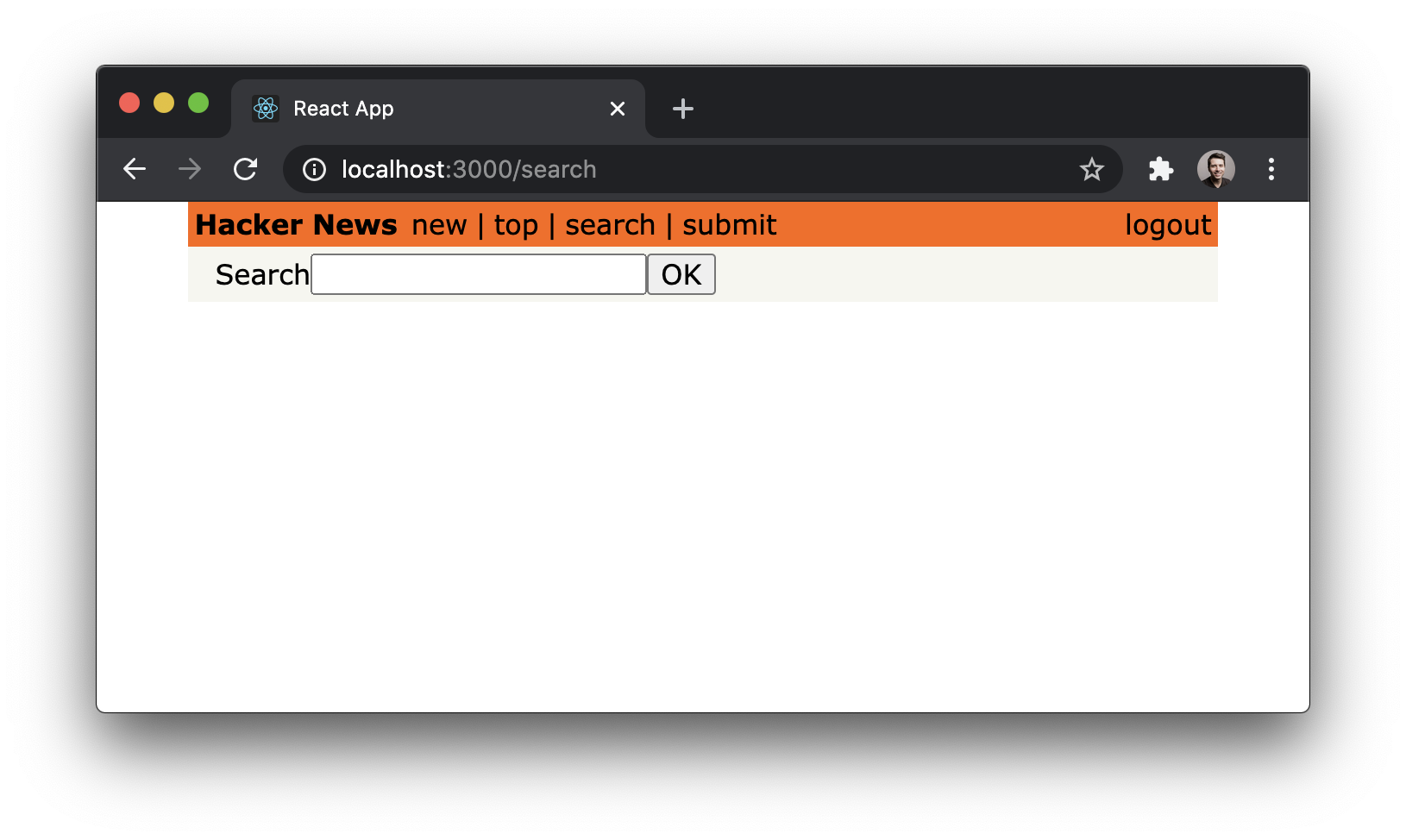
Great, let’s now go back to the Search component and see
how we can implement the actual search.
Filtering Links
This query looks similar to the feed query that’s used in
LinkList. However, this time it takes in an argument
called filter that will be used to constrain the list of
links we want to retrieve.
The actual filter is built and used in the feed resolver
which is implemented in server/src/resolvers/Query.js:
async function feed(parent, args, context, info) {
const where = args.filter
? {
OR: [
{ description: { contains: args.filter } },
{ url: { contains: args.filter } }
]
}
: {};
const links = await context.prisma.link.findMany({
where,
skip: args.skip,
take: args.take,
orderBy: args.orderBy
});
const count = await context.prisma.link.count({ where });
return {
id: 'main-feed',
links,
count
};
}
module.exports = {
feed
};
Note: To understand what’s going on in this resolver, check out the filtering chapter of the Node tutorial.
In this case, two where conditions are specified: A link
is only returned if either its url contains the provided
filter or its description contains the provided
filter. Both conditions are combined using Prisma’s OR
operator.
Perfect, the query is defined! But this time we actually
want to load the data every time the user hits the OK
button, not upon the initial load of the component. To do
this, we’ll use a hook supplied by Apollo called
useLazyQuery. This hook performs a query in the same way
the useQuery hook does but the difference is that it must
be executed manually. This is perfect for our situation––we
want to execute the query when the OK button is clicked.
Let’s include useLazyQuery and execute it when the OK
button is clicked.
const Search = () => {
const [searchFilter, setSearchFilter] = useState('');
const [executeSearch, { data }] = useLazyQuery(
FEED_SEARCH_QUERY
);
return (
<>
<div>
Search
<input
type="text"
onChange={(e) => setSearchFilter(e.target.value)}
/>
<button
onClick={() =>
executeSearch({
variables: { filter: searchFilter }
})
}
>
OK
</button>
</div>
{data &&
data.feed.links.map((link, index) => (
<Link key={link.id} link={link} index={index} />
))}
</>
);
};
The implementation is almost trivial! We’re executing the
FEED_SEARCH_QUERY manually and retrieving the links from
the response that’s returned by the server. These links are
put into the component’s state so that they can be
rendered.
Go ahead and test the app by running yarn start in a
terminal and navigating to http://localhost:3000/search.
Then type a search string into the text field, click the
OK button and verify the links that are returned fit the
filter conditions.