Mutations
Mutation for Creating Links
Setting up mutations is as easy as queries, following a very similar process.
All GraphQL mutations start from a root type called Mutation.
This type is auto generated in the file app/graphql/types/mutation_type.rb:
module Types
class MutationType < BaseObject
# TODO: remove me
field :test_field, String, null: false,
description: "An example field added by the generator"
def test_field
"Hello World"
end
end
end
This type is a placeholder for all GraphQL mutations.
To prevent any error when you first start your GraphQL project, it is generated with a dummy testField field.
You will be able to remove it as soon as you add your own mutation below.
The mutation type is automatically exposed in your schema:
class GraphqlTutorialSchema < GraphQL::Schema
mutation Types::MutationType
query Types::QueryType
end
Resolvers with Arguments
Now add a resolver for createLink.
For this purpose, you’ll use a Mutation class, as mentioned earlier.
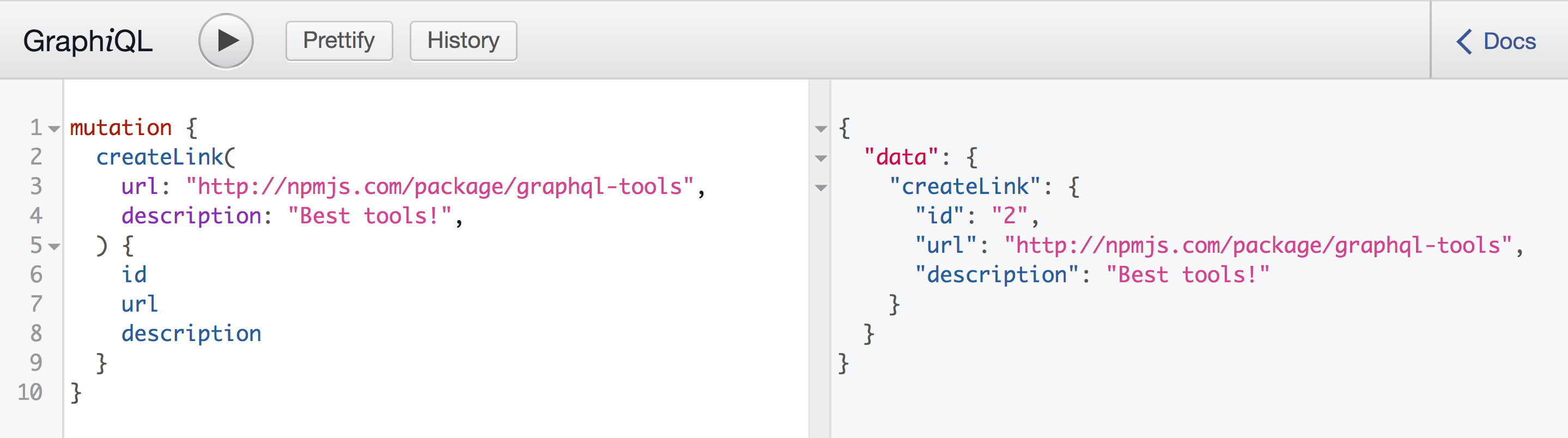
Testing with Playground
To test, just restart the server again and use the new mutation with GraphiQL:
Testing with Unit Test
It’s a good practice in Ruby to unit test your resolver objects.
Here is an example of Resolvers::CreateLink test:
require 'test_helper'
class Mutations::CreateLinkTest < ActiveSupport::TestCase
def perform(user: nil, **args)
Mutations::CreateLink.new(object: nil, field: nil, context: {}).resolve(**args)
end
test 'create a new link' do
link = perform(
url: 'http://example.com',
description: 'description',
)
assert link.persisted?
assert_equal link.description, 'description'
assert_equal link.url, 'http://example.com'
end
end
You can run the tests with the following command:
bundle exec rails test